Why should you receive
herniated intervertebral disc treatment in AMC?
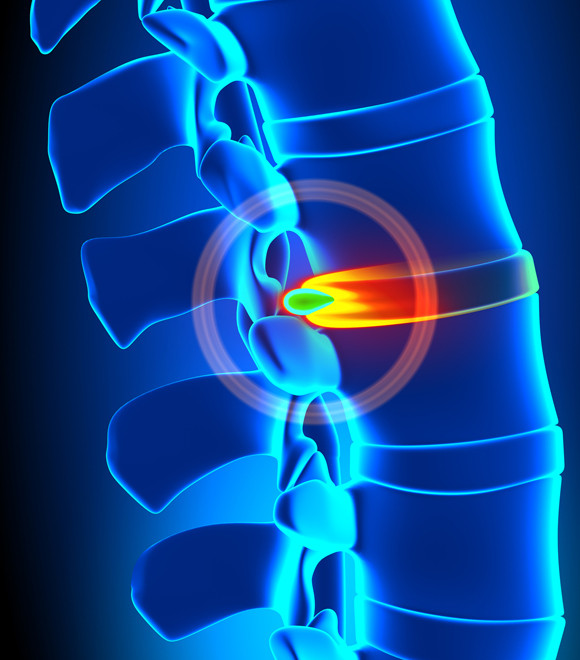
Several small vertebrae come together to serve as a pillar of the body called a spine. In between these small vertebrae are soft jelly-like structures called a ‘disc’ which acts as a cushion that prevents the vertebrae from hitting against each other.
Typically, when a person stands up, the disc in the spine slightly protrudes outward as it is flattened due to the force of gravity. Even if a lot of force is applied, the disc effectively provides cushioning thanks to its unique structure. However, if a person applies an irregular force such as lifting a heavy object or maintaining an incorrect posture for a long period, the disc may protrude beyond normal. In severe cases, the membrane around the intervertebral disc may rupture, resulting in the nucleus pulposus from jutting out.
A herniated intervertebral disc is a classical degenerative lumbar spine disorder characterized by lower back pain that radiates to the lower extremities. In severe cases, it can cause leg paralysis or loss of bowel and bladder control. Vertebral disc disorders are believed that it can be treated and cured easily. However, in reality, the symptoms are like a cycle, improving and worsening repeatedly. Therefore, accurate diagnosis and treatment are necessary. The only problem is that many patients are receiving unproven therapies. Some examples include spinal manipulation, weightless decompression therapy, laser treatment, prolotherapy, etc. These can be a problem because many of these therapies have no clear evidence of being truly effective.
AMC uses evidence-based practices and offers sports therapy as the first line of treatment in collaboration with the sports health center and the department of rehabilitation medicine. If needed, injection therapy is possible with the department of radiology and the department of anesthesiology and pain medicine. At AMC, surgery is recommended only when needed, minimizing the need for unnecessary procedures and surgeries. AMC also actively engages in clinical researches based on the degenerative changes of the intervertebral disc to prevent the cause of disc herniation.
Treatment options

Drug therapy and kinesitherapy
Severe lower back pain and radiculopathy resulting from a lumbar herniated intervertebral disc are mostly caused by an acute inflammatory response, which requires drug therapy to soothe the inflammation. Active lower back exercise is helpful to prevent the recurrence of symptoms.

Nerve injections
After being proven to be an effective method to alleviate local inflammation, nerve injections have become a popular and widely used method to treat herniated discs. Typically, a mixture of a local anesthetic and steroid agent is applied to the area surrounding the nerve roots. Other approaches are also possible as well. However, complications such as inflammation, nerve paralysis, etc. may occur. Also, frequent use of these injections may cause adverse effects such as Cushing syndrome.
Surgery
If unbearable pain persists or if lower extremity paralysis occurs, surgery is the next possible option. Surgical options include making an incision, grinding the bone, pushing aside the nerve, and removing a piece of the protruding disc. Another option is microscopic surgery using a 2cm-sized tube in a method similar to the one mentioned before. Endoscopic surgery may be utilized in some cases. Each approach has its advantages and disadvantages; therefore an appropriate treatment method depending on the location and degree of a protruding disc and the status of the previous operation is considered. If the symptoms repeatedly recur despite surgical treatment, lumbar interbody fusion is performed.
What is a lumbar disc herniation surgery?
-
Operation process
Make an incision → Identify the affected location → Resect the yellow ligament → Push aside the nerve to expose the protruding disc → Cut out the protruding part of the disc → Suture and finish the surgery
-
Surgery Outcomes :
- Pain reduction : Radiculopathy caused by pressing the nerve is dramatically improved.
- Gait improvement : Pain that inhibited the patient from walking properly is reduced and gait is improved.
-
Potential complications :
Patients must be careful after surgery because the possibility of recurrence, inflammation and hematoma are very. Also, patients may feel temporary leg numbness during the operation due to the surgical manipulation of the nerves.
AMC’s treatment performance
- 1989 : Began treatment of lumbar herniated intervertebral discs
- Since 2000 : Began kinesitherapy in collaboration with the Sports Health Medicine Center
- Since 2014 : More than 90% of spinal disc patients have been treated with kinesitherapy and therapeutic injection.
