What is Skull Base Surgery?
Skull base surgery refers to a group of specialized surgical techniques used to access and treat conditions located at the base of the skull, which is the area between the brain and facial structures like the ears, nose, and eyes.
It often involves minimally invasive approaches, using the natural corridors of the nose or small incisions, to access deep-seated tumors or abnormalities in areas that are traditionally very hard to reach. Successful skull base surgery requires extensive collaborative surgical experience between specialists of the Departments of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery and Neurosurgery.
Common Conditions Treated
Otorhinolaryngologists and neurosurgeons work collaboratively to treat the following conditions:
Benign and malignant tumors, such as
- Vestibular schwannomas (acoustic neuromas)
- Meningiomas
- Esthesioneuroblastomas (olfactory neuroblastoma)
- Squamous cell carcinoma, adenocarcinoma, and adenoid cystic carcinoma, nasopharyngeal carcinoma, etc.
- Trigeminal schwannoma
- Pituitary adenomas, craniopharyngioma, Rathke’s cleft cyst, and tuberculum sellae meningioma, and chordoma, etc.
Other conditions
- Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leaks
- Congenital cholesteatoma at Skull base
- Acute/chronic infections or inflammation
- Vascular malformations
Types of Skull Base Surgery Approaches
-
Endoscopic Endonasal Approach (EEA)
- Performed through the nasal passages using an endoscope (camera and instruments).
- Common for tumors and infectious/inflammatory lesions in the pterygopalatine fossa, infratemporal fossa, nasopharynx, parapharynx, pituitary gland, clivus, and anterior/middle/posterior cranial fossa.
- Less invasive, no external incisions, shorter recovery.
-
Transcranial (Open) Approach
- Traditional surgery involving a craniotomy (opening part of the skull).
- Used for larger or more complex tumors that extend into the brain or surrounding structures.
-
Combined or Multidisciplinary Approach
- Otorhinolaryngologists and neurosurgeons often collaborate to access and remove lesions safely.
caption은 테이블마다 수정하는 것을 권장 합니다. Approach Description Main Indications Middle Fossa Approach (MFA) Elevation of the temporal lobe to access the middle cranial fossa and internal auditory canal. - Vestibular schwannoma (with hearing preservation)
- Facial nerve schwannoma
- Lesions in petrous temporal bone
- CSF leak repair
Translabyrinthine Approach (TLA) Posterior approach that sacrifices the labyrinth to access the internal auditory canal. - Vestibular schwannoma (when hearing is already lost)
- Facial nerve tumors
- Lesions of the posterior skull base
Endonasal Endoscopic Approach (EEA) Minimally invasive midline approach via the nasal cavity using an endoscope. - Anterior, middle, and posterior skull base tumors
- Nasopharyngeal tumor
- Lesion in the PPF and ITF
- Pituitary adenoma
- Craniopharyngioma
- CSF leak repair
Role of the Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery in Skull Base Surgery

Otorhinolaryngologists play a key role in
- Accessing to the complex anatomy of the nose, sinuses, ear, and upper pharynx
- Preserving facial nerves, hearing, and sense of smell
- Providing postoperative care including sinus management, speech/swallow therapy, and infection control
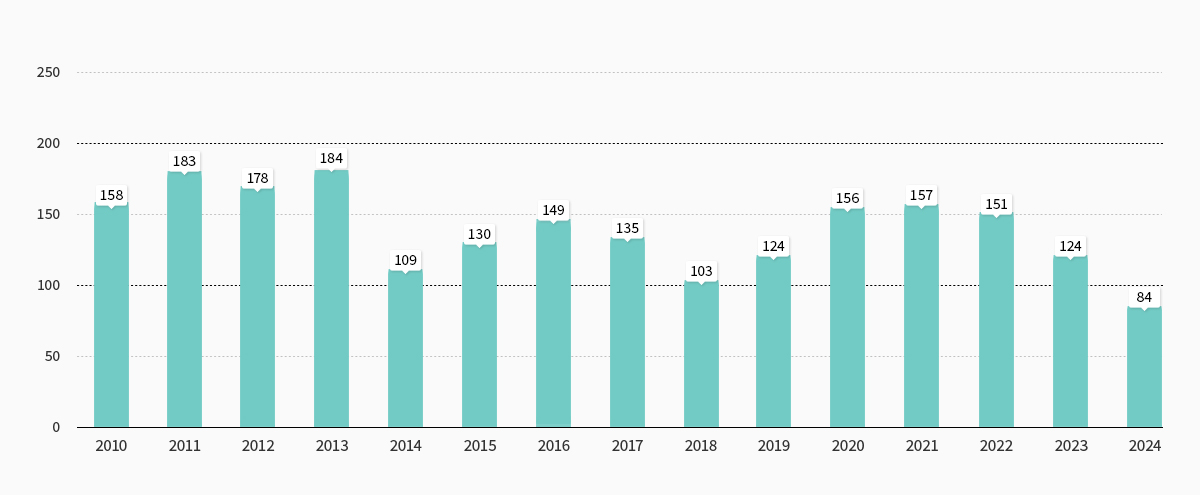
Clinical Performances in the Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery