Orthognathic (jaw) and facial contouring surgery extend beyond aesthetics, playing a vital role in correcting functional issues such as bite misalignment, jaw asymmetry, and airway problems. Advances like cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) and 3D planning software enable precise preoperative visualization, including simulations of bone movements and soft tissue outcomes. Computer-aided design/manufacturing (CAD/CAM) produces custom surgical guides, ensuring precise bone repositioning with minimal soft tissue disruption and concealed (intra-oral) scars. This high-tech approach shortens recovery time and lowers the risk of postoperative complications, with most patients experiencing improvements in chewing, speech, facial harmony, and even sleep quality when surgery addresses sleep apnea. Collaboration among orthodontists, surgeons, and rehabilitation teams ensures holistic treatment.
At Asan Medical Center, we provide comprehensive surgical solutions for individuals with jaw and facial asymmetry, prominent cheekbones, a square jawline, or protrusive lips and chin. Our multidisciplinary approach combines advanced plastic surgery with orthodontic expertise to restore facial harmony, improve function, and boost patient confidence.
Jaw Deformities: Mandibular Prognathism (Underbite)
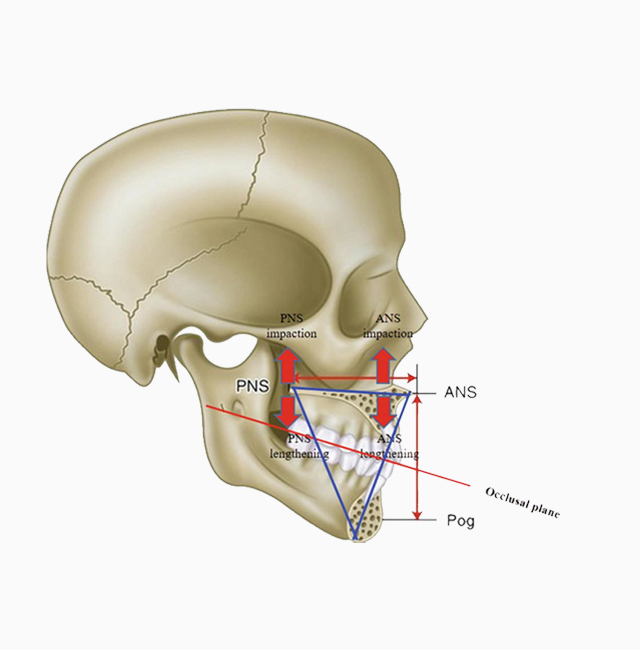
Commonly known as an ’underbite,’ mandibular prognathism refers to the lower jaw protruding beyond the upper jaw. In these cases, the lower teeth typically overlap the upper teeth, leading to malocclusion and aesthetic imbalance. This condition often has a genetic basis, and patients may present with:
- A protruding jawline when viewed from the side
- A reversed bite pattern
- Difficulty closing the mouth naturally
If only the chin is elongated, the condition may be classified as macrogenia, or a long chin, which requires a different treatment approach than full jaw repositioning.
Surgical Correction
Patients with severe skeletal discrepancy require orthognathic surgery, typically the bilateral sagittal split osteotomy (SSRO) to reposition the lower jaw backward. Prior to surgery, orthodontic treatment is necessary to decompensate the dental alignment and optimize occlusion following jaw repositioning.
- Hospitalization : 4–5 days
- Anesthesia : General
- Surgical approach : Intraoral incision with no visible scars
- Jaw fixation : Temporary postoperative intermaxillary fixation may be needed
Bimaxillary Protrusion (Protrusive Lips)
Patients with bimaxillary protrusion often appear to have ’protruding lips,’ caused by forward-positioned upper and lower front teeth and gums. This can result in:
- A ’gummy smile’ when smiling
- Difficulty closing the lips at rest
- A strained appearance of the chin when attempting to close the mouth
- Perceptions of an ’angry’ or ’tensed’ facial expression
Ideal lip position : When viewed from the side, the lips should lie 2–4 mm behind an imaginary line connecting the nasal tip and chin. If the lips lie in front of this line, surgical correction may be considered.
Treatment Options
- Mild cases : Orthodontic treatment alone may be sufficient
- Severe cases : Combined orthodontics and anterior segmental osteotomy (ASO) are needed to reposition both the teeth and underlying bone
ASO Surgery
- Removal of premolars to create space
- Repositioning of the front portion of the jawbone and teeth backward
- Can be combined with chin augmentation or reduction if necessary
Square Jaw (Prominent Mandibular Angle)
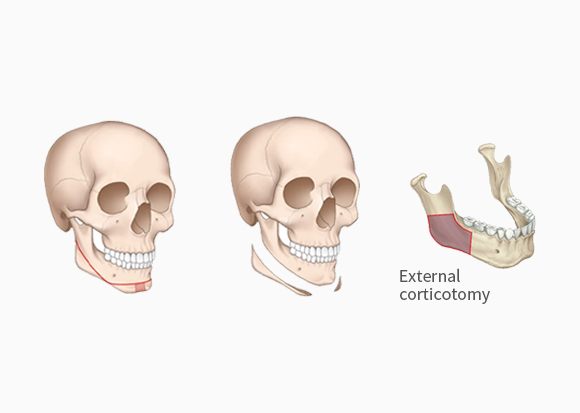
A broad, square-shaped jaw can create a heavy or masculine facial impression, especially when the mandibular angles are prominent on both sides.
Surgical Solutions
- Mandibular angle reduction : Smoothing the prominent angle when viewed from the side
- Cortical bone shaving (corticectomy) : Reducing jaw width when viewed from the front
- May include chin reshaping for balanced facial proportions
Recovery
- Intraoral approach minimizes visible scarring
- Postoperative compression bandages are applied for 1 week
- Minor swelling, bruising, and numbness typically resolve within 2 weeks
Zygoma (Cheekbone) Reduction
Prominent cheekbones, either anteriorly projected or laterally flared, are common in East Asian facial structures and may give a wide and flat facial appearance.
Zygoma Reduction Surgery
- Involves osteotomy to reposition the cheekbone
- Performed through intraoral and small temporal incisions
- Fixation with titanium or absorbable plates as needed
Benefits
- Narrows facial width
- Softens midface prominence
- Often performed in conjunction with jaw surgery for facial harmony
Recovery & Postoperative Care
- Most facial contouring surgeries require 3–5 days of hospitalization
- Swelling peaks on days 2–3, then gradually subsides
- A soft diet is recommended for 2 weeks
- Regular antiseptic mouth rinses help prevent infection
- Return to daily activities and work is typically possible within 10–14 days
Why AMC?
- Integrated Orthodontic & Surgical Planning
- Advanced Imaging and Simulation for precise facial analysis
- Multidisciplinary Collaboration: Plastic Surgery, Orthodontics, Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery (ENT), Psychology
- Natural & Balanced Results with minimal scarring
